본 게시글은 Edwith 문일철 교수님의 데이터 구조 및 분석: Linear Structure and Dynamic Programming을 듣고 정리한 내용입니다.
1. Recursions (재귀호출) Idea
- Repeating problem
ex) 예산이 600만원 있을 때, 전체 예산 기획 과정과 그 하위 부서의 예산 기획 과정은 동일한 문제일 것.
=> 큰 하나의 문제가 정의되면, 그 문제를 쪼개 반복되는 또 다른 문제로 만든다는 것. - Divide and Conquer : 문제를 잘게 쪼개어서 해결하는 과정
- Examples)
- (1) Factorial :
$$ Factorial(n) = \left\{\begin{matrix}1 & \textrm{if } n = 0 \\ n \times (n-1) \times \cdots \times 2 \times 1 & \textrm{if } n > 0 \end{matrix}\right. $$ - Repeating problems : $$ Factorial(n) = \left\{\begin{matrix}1 & \textrm{if } n = 0 \\ n \times Factorial(n-1) & \textrm{if } n > 0 \end{matrix}\right. $$
- (2) Greate Common Divisor(최대공약수)
ex) GCD(32, 24) = 8 - Euclid's Algorithm :
GCD(A, B) = GCD(B, A mod B) = GCD(A mod B, B mod (A mod B))
GCD(A, 0) = A
→ 역시 repeating problem의 구조! - (3) Repeating function calls, Reducing parameters, mathematical inductions, etc...
2. Recursion
- 반복되는 item을 self-similar 방식으로 다루는 프로그래밍 방법.
- function 속에서 function을 call 하는 구조를 주로 사용.
- pseudo code :
def functionA(target):
...
functionA(target)
...
if (escapeCondition):
return A- Example : Fibonacci
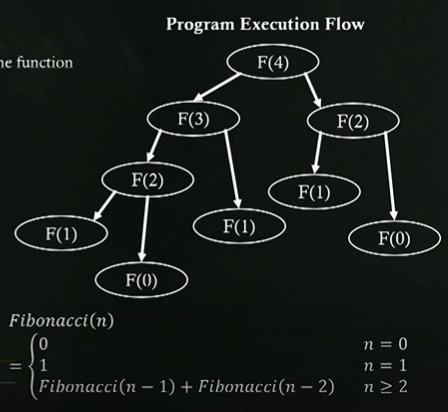
def Fibonacci(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
if n == 1:
return 1
intRet = Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2)
return intRet
for itr in range(0, 10):
print(Fibonacci(itr))
# 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34
- $$ Fibonacci(n) = \left\{\begin{matrix}0 & n = 0 \\ 1 & n = 1 \\ Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2) & n \geq 2 \end{matrix}\right. $$
3. Recursions and Stackframe
- Recursion of functions
- Increase the items in the stackframe
- stackframe : function call history를 저장하고 있는 stack
- push : function이 invoked(call) 되면 push됨.
- pop : function이 return되면 pop됨. - What to store?
- local variable(within function variable)과 function call parameter(특정 function call에 할당된 param)를 저장.
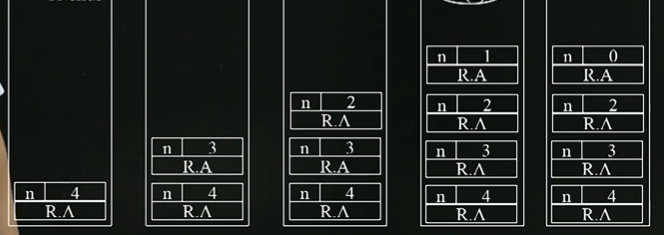
- F(4) 호출과 동시에 저장 -> F(3) 호출과 동시에 저장 -> F(2) -> F(1), 리턴함과 동시에 pop -> F(0), 리턴과 동시에 pop.
앞서 Recursion에 대해 다뤘다면, 이번에는 merge sort 정렬문제에 recursion이 적용되는 예제에 대해 살펴보도록 합니다.
4. Merge Sort
- recursion을 이용한 sorting algorithm의 하나.
- 더 작은 리스트 사이즈로 줄이고 줄여 줄일 수 없는 한 숫자가 됐을 때 부터 비교해 나가며 정렬하는 과정임.
- 다음과 같은 수열이 있다고 했을 때, 딱 중간을 기준으로 쪼갠다. 그 후 다시 merge sort 호출, 또 다시 recursion으로 반쪽으로 자르고 merge sort 호출하는 식으로 진행된다. (Decomposition)
- 모두 더이상 자를 수 없는 상태가 된다면 Aggregation이 진행된다.

import random
def performMergeSort(list_to_sort):
if len(list_to_sort) == 1:
return list_to_sort
sublist_to_sort1 = []
sublist_to_sort2 = []
for itr in range(len(list_to_sort)):
if len(list_to_sort)/2 > itr:
sublist_to_sort1.append(list_to_sort[itr])
else:
sublist_to_sort2.append(list_to_sort[itr])
sublist_to_sort1 = performMergeSort(sublist_to_sort1)
sublist_to_sort2 = performMergeSort(sublist_to_sort2)
idxCount1 = 0
idxCount2 = 0
for itr in range(len(list_to_sort)):
if idxCount1 == len(sublist_to_sort1):
list_to_sort[itr] = sublist_to_sort2[idxCount2]
idxCount2 = idxCount2 + 1
elif idxCount2 == len(sublist_to_sort2):
list_to_sort[itr] = sublist_to_sort1[idxCount1]
idxCount1 = idxCount1 + 1
elif sublist_to_sort1[idxCount1] > sublist_to_sort2[idxCount2]:
list_to_sort[itr] = sublist_to_sort2[idxCount2]
idxCount2 = idxCount2 + 1
else:
list_to_sort[itr] = sublist_to_sort1[idxCount1]
idxCount1 = idxCount1 + 1
return list_to_sort
lstRandom = []
for itr in range(0, 10):
lstRandom.append(random.randrange(0, 100))
print(lstRandom) # [8, 15, 87, 49, 79, 87, 7, 14, 38, 77]
lstRandom = performMergeSort(lstRandom)
print(lstRandom) # [7, 8, 14, 15, 38, 49, 77, 79, 87, 87]5. Problems in Recursions :
- Function call이 너무많다!
ex) Fibonacci : 동일한 값을 얻기 위해 동일한 함수를 너무 자주 call 한다.
Fibonacci(4)만 하더라도 F(0) 2번, F(1) 3번, F(2) 2번을 호출하게 된다. - 이를 없애기 위해 Dynamic Programming을 활용할 수 있다!!
'Algorithm Study' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰] 4장 - 빅오, 자료형 (2) | 2024.03.27 |
|---|---|
| 데이터 구조 및 분석 : Linked List (0) | 2022.12.04 |
| 데이터 구조 및 분석 : Abstract Data Types & List(Array) (1) | 2022.12.04 |
| 데이터 구조 및 분석 : UML notation & Structure and Relationship (1) | 2022.12.04 |
| 데이터 구조 및 분석 : Polymorphism & Abstract Class (0) | 2022.11.20 |



